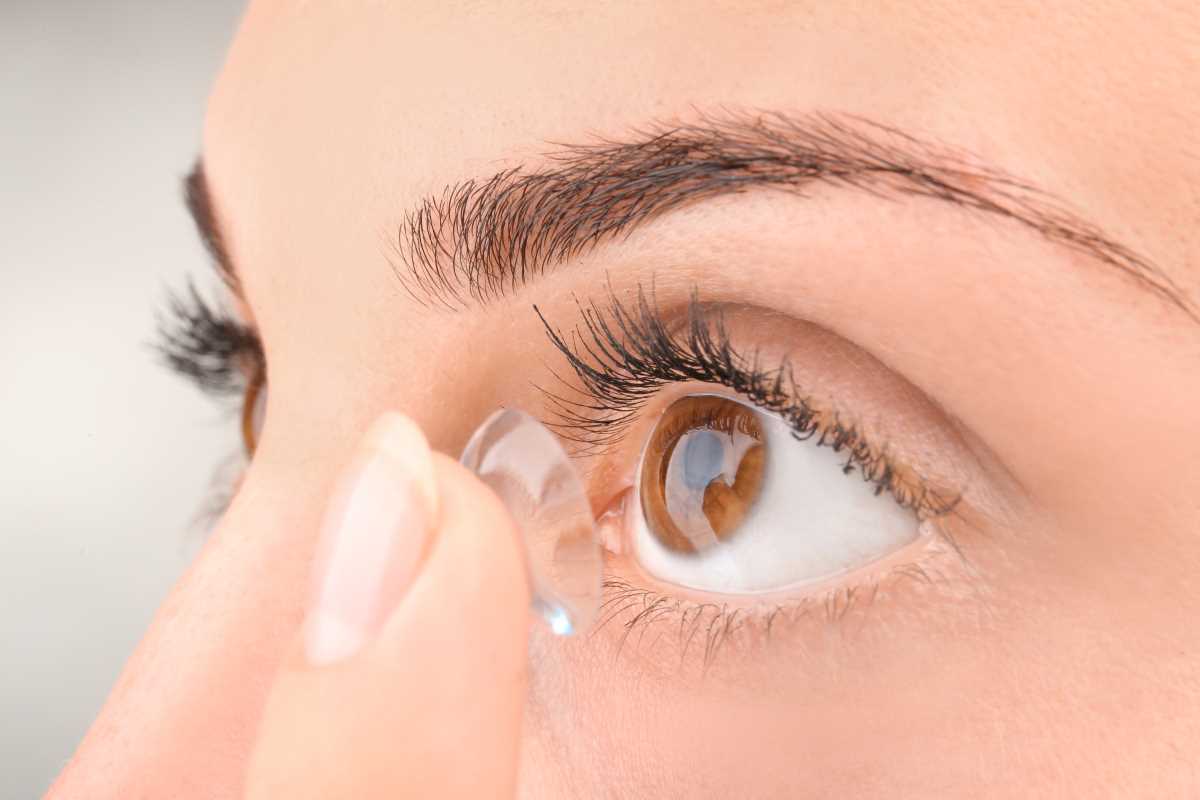
Diabetes management often feels like a balancing act, with blood sugar levels requiring constant attention. For many, traditional glucose monitoring methods like finger pricks can be inconvenient or uncomfortable. Smart contact lenses are emerging as an innovative solution to this challenge. These advanced devices are designed to monitor glucose levels in real-time by analyzing tears. Combining cutting-edge engineering with wearable technology, they aim to make diabetes management faster, easier, and less invasive. Let's talk about how smart contact lenses work and the benefits they offer. We'll also highlight some of the companies leading the way in this groundbreaking technology.
Understanding Smart Contact Lenses and Their Functionality
Smart contact lenses are next-generation wearables equipped with tiny sensors and electronics. Unlike traditional glucose meters that test blood, these lenses analyze glucose concentrations in tears. Tears are easier and less painful to collect, yet still provide valuable health information comparable to blood glucose levels.
How Smart Contact Lenses Work
These lenses rely on biosensors embedded within the lens material. Biosensors measure glucose levels in the tear fluid and transmit data wirelessly to a connected device, such as a smartphone or smartwatch. Some lenses also incorporate micro-LEDs that light up to signal when glucose levels are too high or too low, providing instant visual feedback.
Key Components
- Biosensors: Detect glucose molecules in tears with high sensitivity.
- Wireless Chips: Transmit glucose data to external devices for monitoring.
- Micro Batteries: Power the sensors and data transmission, often fully integrated into the lens.
The compact design keeps the lenses flexible, lightweight, and comfortable, similar to standard contact lenses.
Advantages of Smart Contact Lenses for Diabetics
Managing diabetes requires consistent monitoring, yet many find the current methods inconvenient. Smart contact lenses aim to solve this problem by providing non-invasive, pain-free glucose monitoring.
1. No Finger Pricks
Unlike blood glucose meters, these lenses eliminate the need for frequent blood samples. This is especially significant for individuals who need multiple tests throughout the day.
2. Real-Time Tracking
The continuous nature of glucose monitoring allows diabetics to respond to fluctuations faster, reducing the risk of complications like hyperglycemia or hypoglycemia.
3. Enhanced Convenience
Smart contact lenses integrate seamlessly into daily life. Wearers don’t need to interrupt activities to test glucose levels, making it easier to manage diabetes.
4. Potential for Automated Data Sharing
These lenses can connect to apps that share readings with caregivers or doctors, enabling more personalized care and better diabetes management plans.
Leading Smart Contact Lens Technologies
Although still in the development phase, several companies and research projects are making significant strides in smart contact lens technology. Here are some of the key players pushing this innovation forward.
1. Verily - A Partnership with Novartis
Google’s sister company, Verily, is one of the most well-known names in this field. Verily partnered with Novartis to develop a glucose-monitoring contact lens capable of providing continuous glucose readings through tears.
Features
- Tiny sensors detect glucose levels in real-time.
- Energy-efficient technology for daily wear comfort.
Current Progress
Although Verily paused its project temporarily, the team continues to explore other applications for smart contact lenses, showing that the technology has immense potential in future diabetes care.
2. Sensimed Triggerfish
Unlike other lenses, Sensimed Triggerfish was originally developed for glaucoma patients but demonstrates the potential for similar applications in glucose monitoring. This Swiss company uses cutting-edge sensors to collect various eye-related data, paving the way for future adaptations to include glucose detection.
Features
- 24-hour glucose-related feedback.
- Compatibility with app-based tracking.
3. Scientists at Pohang University of Science and Technology (POSTECH)
POSTECH researchers in South Korea have developed a smart contact lens prototype with glucose-detecting biosensors and micro LEDs.
Features
- Warning system activates LEDs when glucose levels exceed safe thresholds.
- Less reliance on external devices while maintaining high accuracy.
Current Progress
POSTECH’s accomplishments highlight how innovative designs could create user-friendly lenses that work independently of smartphones.
4. Mojo Vision Smart Lenses
This one isn't exclusively for glucose monitoring, but Mojo Vision lenses push boundaries, incorporating AR (augmented reality) capabilities that could be applied to diabetes care in the future.
Features
- Real-time data is delivered directly to the wearer’s vision.
- Compact sensors integrated into a comfortable lens design.
5. South Australian Researchers at the University of South Australia
This group is pioneering printable biosensor technology capable of real-time glucose tracking. Their method uses cost-efficient materials, potentially making smart lenses more affordable.
Features
- Printable sensors embedded within standard contact lenses.
- Connectivity with simple health apps for real-time notifications.
6. Rockley Photonics and Glucose Monitoring Partnerships
Rockley Photonics has developed advanced sensor platforms that may soon integrate with smart lenses for tear-based glucose monitoring. Though focused largely on wrist-based applications, their innovations are likely to extend to contact lens technology.
Features
- High-resolution infrared sensors.
- Compatibility with telehealth systems.
Challenges in Developing Smart Contact Lenses
Despite their promise, smart contact lenses face several hurdles before large-scale adoption becomes possible.
1. Accuracy and Reliability
Tear glucose levels don’t always mirror blood glucose concentrations perfectly. Refining sensor sensitivity will be extremely important for dependable readings.
2. Battery Limitations
Microbatteries powering the devices need to be safe, long-lasting, and efficient without making the lenses bulky or uncomfortable.
3. Cost and Accessibility
Advanced technology often brings higher costs. Manufacturers must focus on producing affordable lenses for accessibility for all diabetics, including those in underserved areas.
4. Regulatory Approvals
Smart contact lenses must meet rigorous safety and efficacy standards before obtaining FDA or global regulatory approval.
 (Image via
(Image via