Robotic surgery is revolutionizing the medical field, becoming a powerful tool for minimally invasive procedures. By combining advanced technology with precision, these systems reduce scarring, speed up recovery, and minimize complications. For patients, this means surgeries that are safer and less intrusive, making the whole process more manageable. The field is constantly evolving, with procedures once reserved for traditional methods now performed robotically. The future of robotic surgery holds the promise of further transforming how doctors approach highly complex surgeries. Here, we’ll explain surgeries that are already performed with robotic assistance and those that could soon benefit from this cutting-edge technology.
Surgeries Already Performed with Robotic Assistance
Robotic surgery systems like the da Vinci Surgical System have been widely adopted in hospitals around the world, offering advantages such as smaller incisions, reduced pain, and faster recovery. Below are some of the most common procedures already carried out with robotic assistance.
1. Prostate Surgery
Prostatectomies, procedures used to remove all or part of the prostate gland, are among the most common robotic surgeries. The precision of robotic tools is especially valuable here as it reduces the risk of nerve damage, helping patients preserve urinary, and function post-surgery. Surgeons use robotic systems to maneuver in tight spaces around the prostate where high levels of accuracy are needed.
2. Hysterectomy and Gynecological Surgeries
Hysterectomies, which involve the removal of the uterus, are now routinely performed with robotic assistance. Robotic surgery also supports other gynecological procedures such as removing ovarian tumors, treating endometriosis, or addressing severe pelvic pain. These surgeries benefit from better visibility and the ability to make delicate movements, reducing complications and recovery time.
3. Cardiac Surgery
Robotic systems assist in minimally invasive heart surgeries, from valve repair to coronary artery bypass grafting. Traditional open-heart surgery often involves large incisions through the chest, but robotic-assisted techniques require much smaller cuts. Benefits include reduced trauma for patients and quicker recovery times, which are important for such life-saving surgeries.
4. Colorectal Surgery
Surgeries involving the colon or rectum, including the removal of cancerous growths or treatment for inflammatory bowel diseases, are commonly performed robotically. These procedures are highly intricate due to the complexity of the digestive system, making robotic assistance a valuable tool for improving outcomes.
5. Hernia Repairs
Robotic surgery is widely used in repairing hernias, allowing for smaller incisions and more precise placement of surgical mesh. Robotic tools provide the surgeon with a magnified view of the affected area, reducing the chance of recurrence or additional complications.
6. Head and Neck Surgeries
Transoral robotic surgery (TORS) has become a reliable option for treating certain head and neck conditions. It is often used to remove tumors in the throat or base of the tongue, offering excellent outcomes by minimizing trauma to surrounding tissues.
The Next Frontier of Robotic-Assisted Surgeries
The potential for robotic surgery extends far beyond its current applications. Surgeons and researchers are exploring new possibilities, with hopes of bringing these groundbreaking systems to more areas of medicine. Here are some of the procedures that could define the future of robotic surgery.
1. Brain and Neurosurgery
Developing robotic systems for brain surgery is a challenge due to the complexity and sensitivity of the brain. Advancements are underway to allow robots to assist in delicate procedures like tumor removal or repairing brain abnormalities. Robotic precision can help minimize damage to surrounding areas, which is important for maintaining neurological function.
2. Lung Surgery
Lung surgeries, including lobectomies to remove cancerous sections, are being tested with robotic systems. Robotic tools could allow for greater maneuverability in the chest cavity, enabling doctors to target specific areas while sparing healthy tissue.
3. Orthopedic Procedures
Robots are already making waves in knee and hip replacements, but future developments could expand their role in repairing fractures or other skeletal injuries. Precision in implant placements during joint surgery reduces wear and tear, potentially extending the life of prosthetics and improving patient mobility.
4. Spinal Surgery
Spinal surgeries often require extreme accuracy to avoid nerve damage. Robotic systems are being developed to assist with procedures such as spinal fusion or correcting scoliosis. Using robotics in this field could lead to a reduction in complications and shorter recovery periods.
5. Pediatric Surgeries
Children undergoing surgery face unique challenges due to their smaller size and ongoing development. Robotic technology is expected to play a key role in expanding minimally invasive options for pediatric surgery, ranging from gastrointestinal procedures to heart repairs, where precision is essential.
6. Transplant Surgery
Organ transplants are some of the most complex surgeries in existence. Using robotic tools during kidney or liver transplants could improve precision in supporting blood vessels and tissues. This could help reduce complications and make recovery smoother for both the donor and the recipient.
Innovations Driving the Future of Robotic Surgery
Progress in robotic systems isn’t limited to expanding the types of surgeries they can perform. Future developments aim to refine how these systems operate, making them more effective and accessible to healthcare providers.
- Smaller Robots: Advances in technology are producing smaller, more agile robots that allow surgeons to work in extremely tight areas. These innovations could make robotic surgery viable for procedures currently too delicate or complex for existing systems.
- AI Integration: Artificial intelligence (AI) is being integrated into robotic surgery systems, enabling smarter tools that adapt in real time. AI could assist surgeons by highlighting problem areas, providing predictive analytics, or suggesting the best surgical approach based on the patient’s unique anatomy.
- Remote Surgery: Telesurgery, where surgeons operate remotely using robotic systems, is already being trialed. This could be a game changer for patients in underserved areas, providing access to top-tier surgical care without the need for travel.
- Haptic Feedback Systems: Advances in haptic feedback systems paired with robotic arms will allow surgeons to “feel” what they’re operating on through the robot, providing heightened precision and improving outcomes in delicate procedures.
Challenges Facing Robotic Surgery
Despite the potential, robotic surgery faces some hurdles that need to be addressed. The high costs of robotic systems are a barrier for many hospitals, limiting access to advanced surgical options. Surgeons also require extensive training to use robotic devices effectively, adding additional investment in time and resources.
Another challenge lies in making sure that robotic systems can function seamlessly in complex and high-stakes settings. Developers are working to fine-tune robotic performance and eliminate risks such as system glitches or delays during procedures.
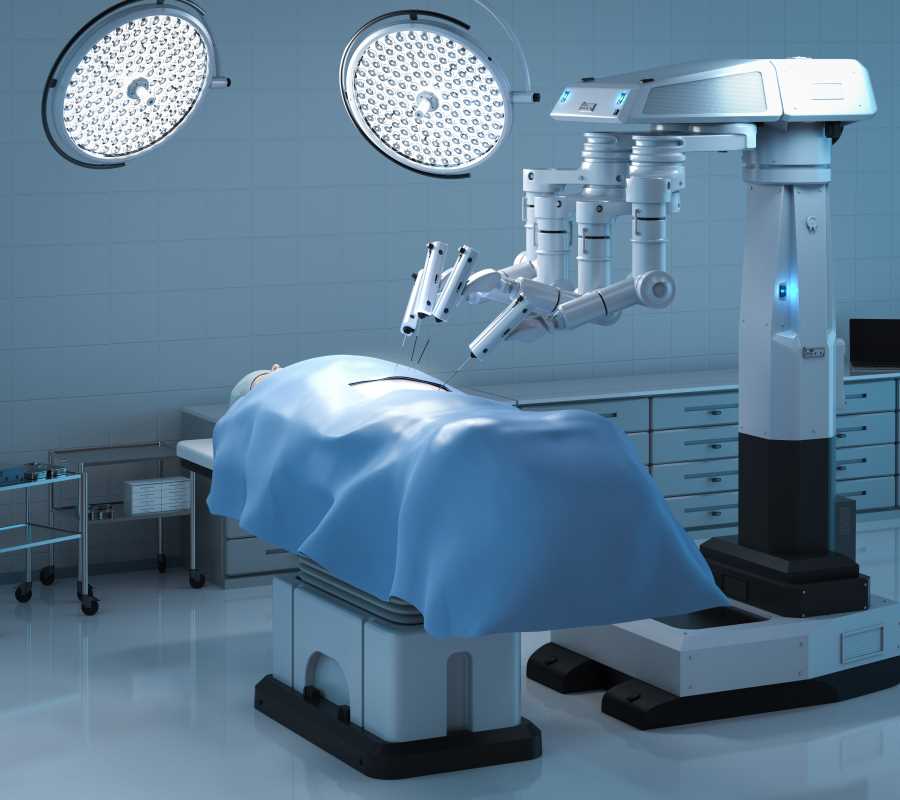 (Image via
(Image via