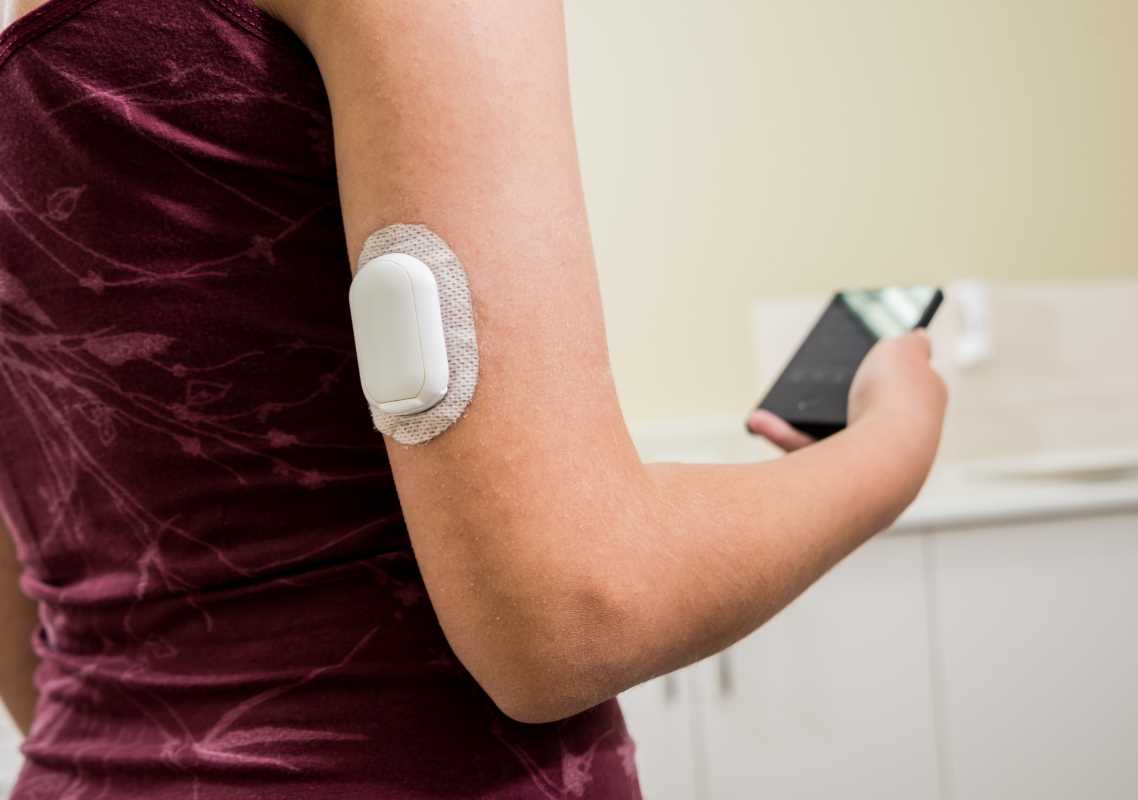
Living with an autoimmune disease often feels like managing an unpredictable daily challenge. These conditions, where the immune system mistakenly attacks the body’s own cells, can cause varying symptoms like fatigue, joint pain, or inflammation. Monitoring these changes could be the answer to managing the disease effectively, but constant check-ins with doctors can be impractical. Enter wearable health technology. New devices are stepping in to track specific symptoms of autoimmune diseases in real time, helping patients and their care teams make informed decisions faster. We're going to check out some innovative wearable devices and the unique ways they monitor symptoms of autoimmune disorders.
1. Abbie by Abbott
Abbie is a wearable companion designed for people managing conditions like rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Tracking symptoms like pain levels and joint swelling has never been easier with this device’s advanced biosensors.
Features
- Constant monitoring of skin temperature and joint-specific pain levels.
- Motion sensors that evaluate joint stiffness and activity limitations.
Benefits
Abbie can identify subtle patterns, such as increased joint swelling, that might indicate a flare-up. For patients with RA, early detection of these symptoms can prevent long-term damage. The device also syncs with an app to provide personalized pain management tips and alerts.
Best For
Rheumatoid arthritis and other joint-related autoimmune conditions.
2. Fitbit Sense 2
Fitbit devices have always tracked activity and heart rate, but the Sense 2 steps up with additional features tailored for autoimmune challenges. This smartwatch is particularly helpful for conditions like lupus or fibromyalgia.
Features
- A stress management sensor uses electrodermal activity (EDA) tracking.
- Measures skin temperature variations and heart rate variability (HRV).
- Tracks sleep patterns and overall physical recovery.
Benefits
Stress and sleep play major roles in triggering autoimmune flares. The Fitbit Sense 2 monitors these metrics and encourages behaviors that keep symptoms in check. It can notify users about persistent stress patterns, helping them adopt relaxation practices before a flare begins.
Best For
Individuals with lupus or fibromyalgia looking to monitor stress and recovery periods.
3. TempTraq Smart Patch
The TempTraq Smart Patch offers unique benefits for people living with autoimmune conditions that cause inflammation, such as Crohn’s disease or ankylosing spondylitis.
Features
- A small, disposable patch that continuously monitors body temperature for up to 48 hours.
- Bluetooth-enabled to sync with a mobile app, offering live updates on temperature trends.
Benefits
Even tiny spikes in body temperature can signal inflammation or an immune response in autoimmune conditions. TempTraq helps users detect these trends early, leading to faster treatment decisions. Its non-invasive design is ideal for continuous monitoring during flares or post-treatment recovery.
Best For
Crohn’s disease, ankylosing spondylitis, or any condition where fever and inflammation are key symptoms.
4. Oura Ring
The Oura Ring focuses on reducing chronic fatigue and improving sleep, two issues faced by people with conditions like multiple sclerosis (MS) or lupus.
Features
- Tracks HRV, body temperature, and sleep stages in a small, ring-sized design.
- Offers daily readiness scores to indicate physical strain and recovery needs.
Benefits
Chronic fatigue is one of the hardest autoimmune symptoms to quantify, but the Oura Ring translates key metrics into actionable insights. Seeing how poorly a patient is recovering overnight, it prompts adjustments to daily routines or physical activity.
Best For
Fatigue-prone patients, particularly those with lupus or multiple sclerosis.
5. KardiaMobile by AliveCor
KardiaMobile is transforming how patients monitor autoimmune-related cardiovascular symptoms, a common issue in diseases like Sjögren’s syndrome or systemic sclerosis.
Features
- A portable electrocardiogram (EKG) that pairs with a smartphone app.
- Detects abnormal heart rhythms, such as atrial fibrillation (AFib).
Benefits
Some autoimmune conditions cause inflammation in blood vessels or directly impact the heart. KardiaMobile provides real-time heart rhythm tracking, giving patients actionable alerts to prevent severe complications, such as stroke or heart attack.
Best For
Autoimmune diseases with cardiovascular complications, including Sjögren’s syndrome and systemic sclerosis.
How Wearables Benefit Autoimmune Patients
By focusing on continuous, real-time monitoring, wearable devices improve the way autoimmune conditions are managed. Key benefits include:
- Early Detection of Flare-Ups: Wearables track subtle trends, giving patients and doctors an early warning system for impending flares.
- Data-Driven Treatment Plans: Comprehensive health data enables precise adjustments to treatments, enhancing their effectiveness.
- Easier Self-Management: Notifications and feedback help patients take proactive steps to prevent symptoms from escalating.
Challenges and Considerations
Despite their promise, wearable devices for autoimmune conditions come with some caveats. Improper calibration, inaccurate readings, or inconsistent use can limit their effectiveness. Patients should also check whether their device is covered by insurance, as some models might be considered non-essential.
Integration with medical professionals is another challenge, but many doctors are seeking additional ways to support their patients beyond medication.
The Future of Wearable Tech for Autoimmune Diseases
Advances in wearable technology promise even more personalized and predictive health management for autoimmune patients. Devices are incorporating AI-powered insights for a deeper understanding of rare symptoms. Future wearables may:
- Feature microfluidic sensors for real-time inflammation monitoring through sweat.
- Use machine learning to predict flares based on diverse health inputs.
These innovations will further narrow the gap between symptom onset and treatment, providing patients with more information than ever before to make educated decisions on their health.
 (Image via
(Image via