Cholesterol is often misunderstood. It’s not entirely bad, but too much of it, especially the wrong kind, can put your health at risk. Statins are medications designed to help manage cholesterol levels, giving your body a better balance of the types you need. These drugs are widely prescribed to lower harmful cholesterol and reduce the risk of heart disease. But how exactly do they work? The process involves blocking a key enzyme, aiding your liver in its cleanup efforts, and even offering some surprising additional benefits. Here’s everything you need to know about how statins make a difference in cholesterol management and why they’ve become a staple in modern medicine.
Understanding Cholesterol Basics
Cholesterol is a waxy, fat-like substance found in your blood. It plays an essential role in building cell membranes, producing hormones, and even helping your body make vitamin D. But not all cholesterol is created equal.
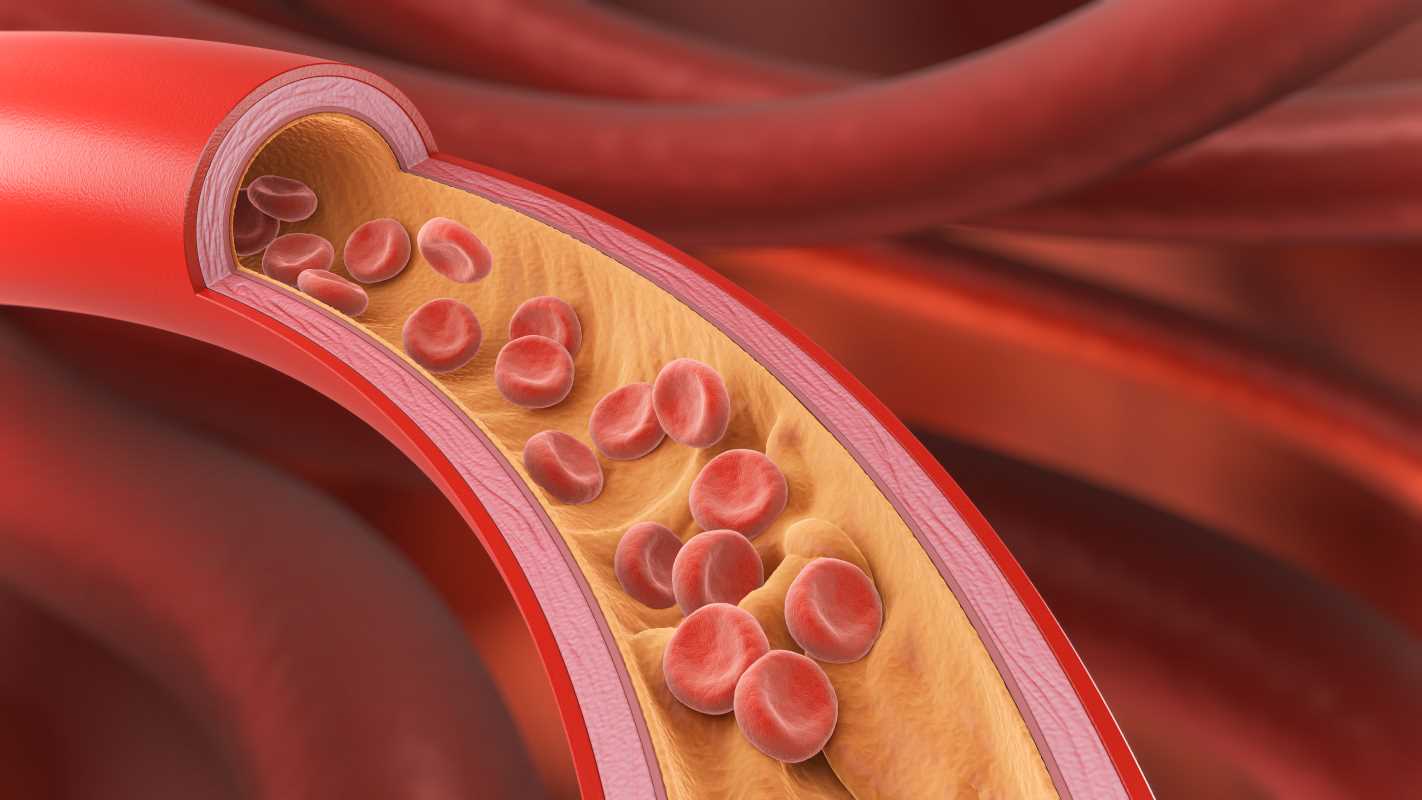
- LDL (Low-Density Lipoprotein): Often called “bad cholesterol,” LDL contributes to plaque buildup in arteries. This buildup can lead to blockages, increasing your risk of heart attacks and strokes.
- HDL (High-Density Lipoprotein): Known as “good cholesterol,” HDL helps remove excess cholesterol from the bloodstream, carrying it to the liver for disposal.
When LDL levels get too high or HDL levels drop too low, it can spell trouble for your cardiovascular system. This is where statins step in to restore balance, lowering cholesterol in your bloodstream and reducing the chance of plaque buildup in your arteries.
But statins don’t stop there. They also help your body get rid of existing LDL. Think of your liver as a cleaning crew for your blood. Statins enhance its ability to “vacuum up” LDL, pulling it out of your bloodstream and turning it into waste.
Digging Deeper Into the Science
Statins function like a dimmer switch for cholesterol production. They don’t shut things off completely since your body still needs a certain amount of cholesterol to function. Instead, they lower production to a safer level and boost LDL receptors in the liver. These receptors are like tiny catchers that help trap and remove LDL particles. The fewer LDL particles floating around your bloodstream, the less likely they are to stick to artery walls and create blockages.
Many statins don’t just alter LDL levels. They also have a modest effect on raising HDL cholesterol and lowering triglycerides, which are another type of fat in the blood. This multi-faceted approach makes them highly effective in overall cholesterol management.
Benefits Beyond LDL Lowering
Statins offer benefits beyond cholesterol management. Research shows that they also help reduce inflammation in the arteries, which plays a big role in heart disease. By calming down inflamed areas, statins make it harder for plaques to rupture, an event that can trigger heart attacks or strokes. Some other benefits include:
- Improved Blood Vessel Function: Statins enhance blood vessel flexibility, improving overall circulation. Healthy, responsive blood vessels are less likely to contribute to high blood pressure.
- Lower Risk of Blood Clots: By reducing the stickiness of platelets in the blood, statins prevent clots from forming unnecessarily. Blood clots can block arteries, leading to serious cardiovascular events.
These added benefits make statins a go-to tool for managing cholesterol and overall heart health.
Commonly Prescribed Statins
Several types of statins are available, varying in strength and how they’re processed in the body. Some of the most common include:
1. Atorvastatin (Lipitor)
Key Features:
- One of the most commonly prescribed statins worldwide.
- Effective at lowering LDL (“bad cholesterol”) levels by up to 55%.
- Can also raise HDL (“good cholesterol”) levels slightly and reduce triglycerides.
Benefits:
- Versatile for patients with diverse cardiovascular risks, including those who have already had heart attacks or strokes.
- Works well at higher doses for significant cholesterol reduction.
Considerations:
- May cause mild side effects like muscle aches or nausea in some users.
2. Simvastatin (Zocor)
Key Features:
- A well-established statin often used for mild to moderate cholesterol issues.
- Reduces LDL levels effectively and provides good results for patients at standard doses.
Benefits:
- A go-to choice for doctors initiating statin therapy for first-time users.
- Generic versions make this medication a more affordable option for many patients.
Considerations:
- Higher doses can increase the risk of side effects, such as muscle pain or weakness.
3. Rosuvastatin (Crestor)
Key Features:
- Known for its high potency, reducing LDL cholesterol by up to 63% at its maximum dose.
- Can help significantly in lowering triglycerides and slightly increasing HDL levels.
Benefits:
- Ideal for patients with very high cholesterol levels or severe cardiovascular risks.
- Administered at lower doses with fewer side effects compared to some other high-potency statins.
Considerations:
- May require regular liver function checks in some patients to monitor for rare complications.
4. Pravastatin (Pravachol)
Key Features:
- A statin with a milder profile, effective for lowering LDL and is gentler on the liver and muscles.
- Often used in individuals who experienced side effects with stronger statins.
Benefits:
- Causes fewer interactions with other medications, making it a safe choice for patients on multiple prescriptions.
- A good option for patients with chronic liver conditions like non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.
Considerations:
- May not be as effective in patients needing significant LDL reductions compared to more potent statins.
Each statin works similarly, but doctors choose specific ones based on the patient’s individual needs, goals, and health history.
Potential Side Effects
Like any medication, statins come with their share of possible side effects. Most are mild and temporary, with symptoms often improving as the body adjusts. Common side effects include:
- Muscle pain or weakness
- Mild digestive issues like nausea or constipation
- Headaches
Rarely, statins might cause liver enzyme changes, which is why doctors monitor liver function during treatment. If side effects become bothersome, adjusting the dosage or switching to a different statin can often resolve the issue.
Who Can Benefit Most?
Statins are recommended for people with high LDL cholesterol levels or those with conditions that increase cardiovascular risk. They are particularly beneficial for:
- Patients with Heart Disease: Statins help stabilize existing plaques, preventing further complications.
- Individuals with Diabetes: Diabetes increases cardiovascular risk, even when cholesterol levels appear normal. Statins offer extra protection.
- People with a Family History of High Cholesterol: Genetic predispositions can make it harder to manage cholesterol naturally. Statins provide a tailored solution.
Doctors may also recommend statins as part of a larger treatment plan that includes diet, exercise, and other medications.
Innovation in Statin Treatments
Statin research is ongoing, with new delivery methods and combinations being explored to improve effectiveness and reduce side effects. Scientists are also working on pairing statins with other cholesterol-lowering treatments, such as PCSK9 inhibitors, for patients who don’t respond well to traditional methods.
Some studies are even investigating nutraceuticals, natural compounds combined with statins, to maximize results in reducing dependence on pharmaceuticals.
 (Image via
(Image via